When you are interested in needing to buy some LED strip lights for use, have you ever worried about what the quality situation of these strips is like? How long can they last after installation? How do you come to judge the quality of these LED light strips? I believe that many people will have these questions because there are too many manufacturers in the market, each with different prices, and what you need is to buy quality and affordable LED strip lights.
LED strip lights all have to be rigorously designed and rigorously tested before they can be considered a good product.
What are the main items in the production test of LED strip lights?
Electrical Performance Test
Verify whether the working current under the rated voltage is in accordance with the standard, measure whether the actual power is consistent with the nominal value, and ensure that the energy consumption meets the design requirements.
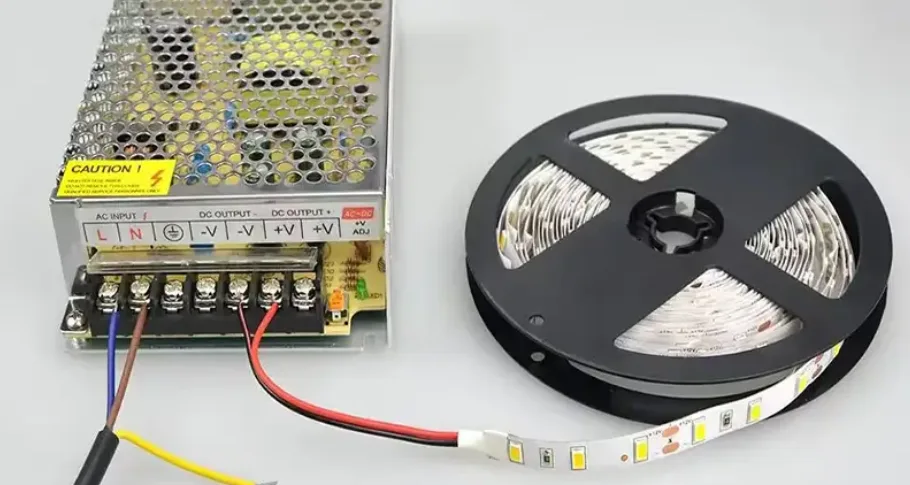
Low-voltage LED strip with DC power supply and multimeter test, according to the multimeter current reading and voltage, using the formula P = UI to calculate the power of the strip; high-voltage LED strip with AC power supply, using an electronic power meter to directly test out the value of the power and power factor size. Measure whether the actual power is consistent with the nominal value to ensure that the energy consumption meets the design requirements.
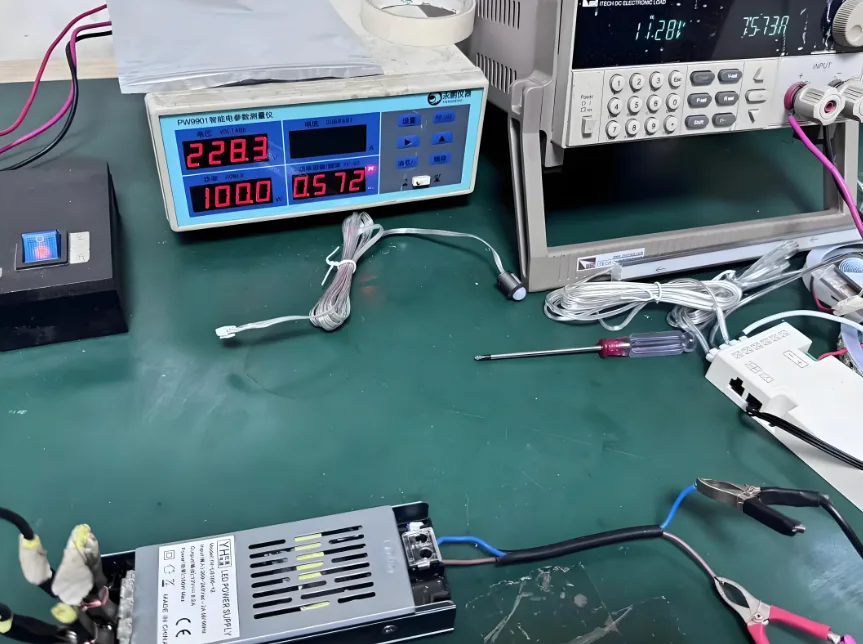
Luminous Efficiency Performance Test
including color coordinates, color tolerance, color rendering index, luminous flux, luminous efficiency, and color temperature. Test using a photometer or integrating sphere system. Measure light output with an integrating sphere or photometer to ensure brightness uniformity. Verify that the color temperature, color rendering index, and color tolerance are in accordance with the nominal values, e.g., 3000K warm light, 6000K cold light, CRI ≥ 80, and SCDM ≤ 3, to ensure that the color is uniform and free from deviation.

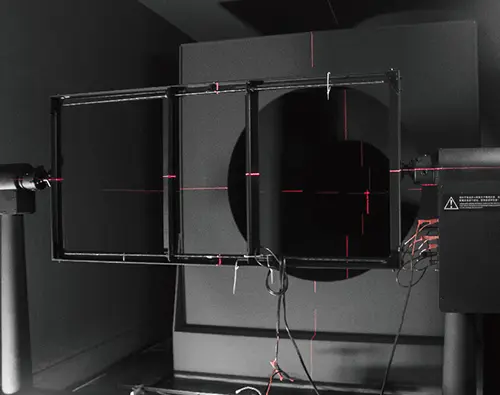
Environmental Adaptability Test
1) High and low temperature cycling test: Use the high and low temperature test chamber to simulate the working condition of LED strip lights under extreme temperatures (e.g., -20℃~+50℃) to test the weather resistance of the strip lights. The LED strip is placed into the temperature-adjustable test chamber and cycled from -20°C to 50°C. The strip needs to be kept at high and low temperatures for 0.5 hours each, cycling 8 times. After the test, the light strip can not have electrical abnormalities such as leakage and non-lighting.
2) High and low temperature working test: The test temperature is at -25℃ and +40℃, and the test time is 96±2 hours.
3) Vibration impact test: Put the LED strip packaged on the vibration test bench, start the vibration meter, speed 300 rpm, amplitude 2.54 cm. In the up and down, left and right, and before and after, the three directions were tested for 30 minutes. Requirements for the strip are that it can not have parts off, structural damage, or other abnormal phenomena. Vibration tester to simulate the mechanical working state of the LED strip in the transportation or installation process, simulate the vibration of the transportation process, fall, and verify the packaging protection performance.
4) Waterproof performance test: Detect the waterproof grade and sealing performance of the LED strip. Use the waterproof test device for immersion or water spray tests.
5) Salt spray test: Evaluate the corrosion resistance of LED strip lights in a salt spray environment in a salt spray test chamber.

Lifetime Test
1) Aging test: Initial luminous flux, power, color temperature, and other parameters are tested at room temperature (25°C). Place the LED strip samples in the same environment and turn on the power to light the lamp. Test every 10 days for the first three months and then once a month. Luminous flux decay to the initial 70% of the strip life; record the average life of all samples.
2) Accelerated life test: In the temperature of 60 ℃ ± 3 ℃, the maximum relative humidity of 60% of the environment without convection wind, the LED strip of rated voltage and rated frequency power supply is applied to the continuous operation of 360 hours. Its luminous flux is not less than 85% of the initial luminous flux. Through high temperature, high current, and other accelerated aging, simulate the life of the LED strip under long working conditions.
3) UV resistance test: Tested by UV aging tester.
Mechanical Performance Test
1) Bending/Folding Test Repeatedly bending to test the flexibility of the LED strip to verify the flexibility of the flexible strip and the reliability of the solder joints after repeated bending.
2) Waterproof grade test: For outdoor LED strips, using a waterproof test device for immersion or water spray test, test IP65 (dustproof and waterproof) or IP67 (anti-submergence) grade.
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Test
1) Electromagnetic interference (EMI) test: Ensure that the light strip will not cause interference to other equipment when working.
2) Anti-interference test: Verify the stability of the strip under external electromagnetic interference.
Environmental Protection Test
Detect whether it complies with RoHS, REACH, and other environmental standards (e.g., lead-free, no hazardous substances).
Through the above tests, the quality of the strip and the user experience can be fully guaranteed. The actual test items may be adjusted according to the product type (e.g., RGB strip, COB strip) and application scenarios (indoor/outdoor).
SignliteLED is a high-tech enterprise specializing in the research, development, and production of LED strip lights, adhering to the “quality-oriented, responsibility first” business philosophy.
The company has more complete production and testing equipment, equipped with an integrating sphere, EMC test, luminosity distribution test instruments, and other optical laboratory production lines with automatic placement machines, aging test rooms, etc., adhering to the whole process of quality control and the use of automated production lines to ensure product reliability.
Many of our products have passed TUV, ETL, UL, and other certifications; our products are widely used in commercial lighting, architectural lighting, and other fields, and our cooperative customers cover more than 10 countries, and we have won the recognition of the market for our stable performance and energy-saving advantag.
Why should LED strip lights do temperature rise tests?
Although the LED light strip has a certain high-temperature resistance, a long time in a high-temperature environment will still have a negative impact on its performance and life. When the temperature exceeds the tolerance range of the LED strip, it may lead to discoloration, reduced brightness, or even blackening of the strip. In addition, high temperature will accelerate the aging of LED beads and shorten their service life.
The main purpose of the temperature rise test is to detect the temperature change of the LED strip under normal operation and simulated fault conditions to ensure that it operates within the safety standards. Excessive temperatures may lead to deterioration of insulation materials, circuit failures, and even fires, posing a threat to user safety.
In addition, the temperature rise test can also assess the thermal stability of LED light strips, discover potential thermal risks in time, and take appropriate heat dissipation measures to ensure the safety performance and durability of the light strips. LEDs are more sensitive to temperature, and high temperatures can seriously affect their service life. Therefore, the temperature rise test is one of the important items in the safety test of LED light strips.
In the temperature rise test, LED strip samples should be placed in a temperature of 25 ℃ ± 2 ℃ and humidity of 50%-90% RH environment for 10 hours to ensure that the surface temperature of the strip samples reaches a balance with the room temperature before testing. The temperature rise test is usually measured using the thermocouple method. During the test, thermocouples need to be placed at critical parts of the LED, such as the location of the pads, to monitor the maximum temperature change in these parts.
The temperature rise test standards for LED strip lights mainly refer to the IEC/EN 60598-1 standards, which specify the general requirements and test methods for LED luminaires. During the test, it is necessary to make the light strip work at maximum power consumption in a specific temperature environment (usually 25±5℃) and record the temperature every 30 minutes until the temperature of each measured part is constant. The record includes the energizing time, the temperature of the measuring parts, and the ambient temperature at that time. The temperature rise of each component shall not exceed 40°C.
Generally speaking, the normal operating temperature range of the LED strip is between -20℃ and 65℃. Within this temperature range, LED light strips are able to maintain stable performance and life. However, the high temperature resistance of LED light strips may vary between different types, manufacturers, and wattages. Therefore, when choosing LED strip lights, you should pick the right product according to the specific use scenario and environment.
The temperature rise test is a key link in the design and quality control of LED strip lights, which is directly related to the safety and reliability of the strip light and is an important basis for LED strip lights to get market access.
How long will the lifespan of LED strip lights be?
LED strip lights usually have a nominal life of 25,000 to 50,000 hours, but in practice, they may be affected by a variety of factors. For example, the quality of the driver power supply, heat dissipation, the usage environment such as temperature and humidity, and the frequency of usage.
High-quality LED strip lights can reach 50,000 hours under ideal conditions, but the actual lifespan is usually 3-10 years, depending on the usage habits and environment. That is, if you turn on the LED strip light for 8 hours a day, 50,000 hours is about 17 years, but in reality, it may not be reached, because the nominal life usually refers to the time when the light decay is up to 70%, not the time when it is completely broken.
The light decay life of an LED strip is usually the time it takes for the brightness to decay to 70% of its initial value, not complete failure. For example, brightness may decrease after 50,000 hours! However, this is not to imply that after this time the LEDs do not light up. After 50,000 hours, the brightness may have decreased by 30%, but they can still be used. As they reach the end of their life, they begin to dim.
What factors affect the life of LED strip lights?
The life of LED strip lights is affected by a variety of factors, mainly including the following aspects.
1. The Quality of Core Components
LED chip quality: poor-quality chips with low luminous efficacy, heat generation, and easy-to-appear light failure or early damage.
Driver power quality: Poor quality power supply easily leads to voltage instability and shortens life (quality power supply can enhance stability by 30%-50%).
2. Unreasonable Circuit Design
The LED drive current design is too large, beyond the stability of the LED current; the LED long-term work in the high-current state generates excessive heat; the line layout is unreasonable; the use of FPC flexible board copper foil is too thin; and the LED heat dissipation effect is poor. These will directly make LED lights work unstably or light failure decline faster, seriously affecting the life of the strip.
Packaging materials: LED light strip LEDs material selection error; the light strip needs to correctly select the PPA material LEDs. If the choice of PCT or EMC, etc., will cause the strip’s bending and flexibility deterioration, it is easy to age at high temperatures and become brittle, and the LEDs are very easy to damage and become ineffective.
For more information on LED packaging materials PPA, PCT and EMC comparisons, read the article How to Choose the Right LED for LED Strip Lights.
3. Insufficient Heat Dissipation Design
If an LED strip light is installed densely or not equipped with a heat dissipation aluminum tank, the internal temperature rise will accelerate component aging. Ambient temperature: High-temperature environments (e.g., direct sunlight areas) will aggravate the accumulation of heat and shorten the life.
4. Poor Power Supply Stability
In areas with large voltage fluctuations, too high a voltage may cause the LED to burn out, and long-term instability will damage the driver circuit. In addition to the use of a poor-quality power adapter, resulting in unstable power output or a surge, will also increase the risk of failure.
5. Continuous Working Hours
Frequent switching of LED strip lights has less impact, but long-term 24-hour continuous use may accelerate the light decay. 24 hours of uninterrupted use is more likely to accumulate thermal stress than intermittent use. If the strip is always on 24 hours, the life may be shortened to 3-5 years. In addition, frequent adjustment of the brightness of the strip or high-frequency flashing may accelerate the fatigue of the electronic components and accelerate the aging of the electronic components.
6. Environmental Factors
Usually, if the LED strip is working in a high-temperature environment for a long time (e.g., >40°C), it will accelerate the aging of the LEDs; non-waterproof LED strips are susceptible to moisture short-circuiting in humid environments (e.g., IP20 is not suitable for bathrooms/outdoors). Excessive dust accumulation affects the heat dissipation of the strip, while the environment containing chemical corrosive gases can cause LED color temperature drift or damage to the circuit and solder joints.
7. Installation and Maintenance
A tight fit on impermeable surfaces (e.g., wood cabinets) impedes heat dissipation, and the use of heat-dissipating LED aluminum channels is recommended. Dust covering the surface of the strip will reduce the heat dissipation efficiency and needs to be cleaned regularly. For outdoor use, choose an IP65 or above rating, and check whether the sealant is aging. Excessive bending, squeezing, or external impact during installation may lead to breakage of the electronic circuit of the LED strip.
How to understand the test of the LM-80 report?
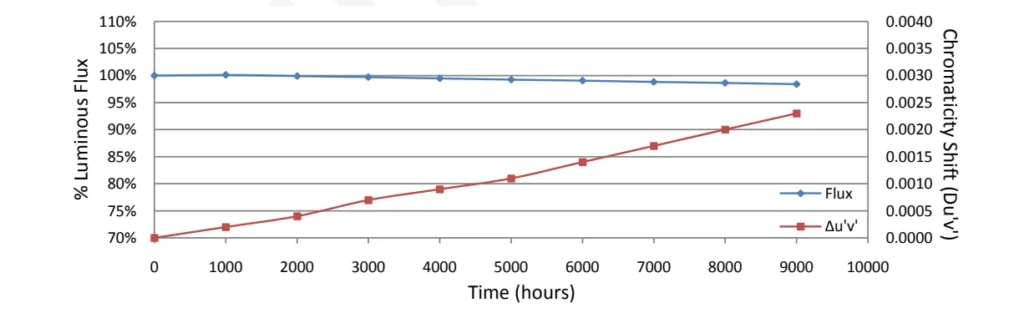
The LM80 report for LEDs is a test standard in the LED industry, developed by the U.S. Energy Star (ENERGY STAR), which is mainly used to evaluate the light degradation of LED light sources after a long period of time.
LEDs, as the core component of LED light strips, have a direct impact on the life span and efficiency of the entire light strip. The report of luminous flux maintenance rate (e.g., “L70” indicates the time for the brightness to drop to 70% of the initial value) and color temperature stability (whether the color is shifted or not) is a comparison of the attenuation trend at different temperatures, which is recognized as an important basis for testing in the industry, and so the LM80 report is important to both manufacturers and consumers.
The LM80 test is a voluntary, non-mandatory test. In addition, a complete LED luminaire life assessment needs to be combined with other test methods, such as TM-21 extrapolation, of which LM80 is only a part.
The LM80 report tests the luminous flux maintenance (i.e., the degree of brightness degradation) of an LED light source by simulating a long-term use environment to ensure that it remains sufficiently bright over its claimed lifetime (e.g., 25,000 hours, 50,000 hours).
Temperature control: LED beads should be tested at a minimum of three temperatures (e.g., 55°C, 85°C, and an intermediate temperature), as high temperatures can accelerate light degradation and shorten the test time.
Test duration: At least 6,000 hours of continuous testing (about 250 days), with some manufacturers extending this to 9,000 hours or more to increase data reliability.
Importance of the LM-80 report: To prove that LEDs comply with international standards and enhance market competitiveness. Avoid early failure of LED lamps due to rapid light decay, ensuring long-term cost-effective use. It is one of the necessary conditions to apply for ENERGY STAR or DLC certification.
Note:
1. LM80 ≠ fixture life; LM80 only tests the LED light source (bead or module), not the complete LED fixture. The actual LED luminaire life is also affected by the driver power supply, heat dissipation design, and other factors. 2.
2. Combined with TM-21 projections, it is usually necessary to extrapolate the LM80 data through the TM-21 standard to estimate the light degradation of a longer period of use (e.g., 50,000 hours).
3. Voluntary testing: LM80 is not mandatory, but high-quality LED products will generally provide this report. When choosing LED products, it is recommended to give preference to brands that have passed the LM80 test.
The LM80 report is to assess the reliability of LED lamp beads “medical report” through rigorous long-term test data to help users determine whether the actual performance of the LED publicity commitment. When purchasing LED strips or other LED lamps and lanterns, it is recommended to pay attention to whether they have LM80 certification and testing conditions to ensure long-term use.
How to make LED strip lights last longer?
Choose a brand power supply, such as Philips, Meanwell, or OSRAM, and LED chips from Philips, Samsung, CORE, etc. Quality is more reliable.
Ensure heat dissipation: Install on metal or heat dissipation LED channel; avoid confined spaces.
●Environmental control: Avoid high-temperature and high-humidity areas such as bathrooms, kitchens, etc., or choose products with corresponding protection levels.
●Correct Installation: Avoid bending the strip too much to prevent wiring damage.
●Stable power supply: Use a regulated power supply or constant current driver to avoid over-voltage use.
●Control the usage time: Set the automatic switch for non-essential scenes to reduce the continuous high-temperature operation.
By optimizing the above factors, the life of the strip can reach more than 20,000 hours (about 5-10 years), but the actual use of the light should be combined with specific scenarios to adjust the maintenance strategy.
What are the certification standards for LED light strips?

As an electrical lighting product, LED strip lights need to meet the appropriate safety and quality standards when sold in different countries and regions, and common test certifications include the following categories.
1. Mandatory Safety Certification
China: CCC certification (China Compulsory Certification) applies to domestic sales of light strips; they need to pass the electrical safety, electromagnetic compatibility, and other tests.
EU: Low Voltage (LVD Directive), Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC Directive), and Environmental (RoHS, REACH) requirements.
North America: UL certification (U.S.) / CSA certification (Canada) UL 588 (Holiday Strip Lights), UL 2108 (Low Voltage Strip Lights), or UL 1598 (Fixed Installation Strip Lights) are common standards.
Japan: PSE certification, round PSE (voluntary) or diamond PSE (mandatory), depending on product power and type.
2. Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Certification
FCC certification (USA) ensures that the product complies with electromagnetic interference (EMI) standards.
CE-EMC (EU) meets the EMC Directive (2014/30/EU).
3. Environmental Certification
RoHS (EU) restricts the use of lead, mercury, and other hazardous substances.
REACH (EU) regulates the safe use of chemical substances.
WEEE (EU) regulates the recycling of electronic waste.
4. Energy Efficiency Certification
Energy Star (U.S./Global) certification for energy efficiency performance.
The ERP Directive (EU) requires compliance with energy efficiency labels (e.g., luminous efficacy, lifetime, strobe, etc.).
5. Other Special Certifications
IP protection level for outdoor or wet environments with waterproof and dustproof performance (such as IP65 or IP67).
IEC/EN 60598 international general safety standards for lamps and lanterns.
Explosion-proof certification (e.g., ATEX, EU) for explosion-proof light strips used in hazardous environments (e.g., chemical industry, mines).
6. International General Standards
IEC standards such as IEC 62471 (photobiological safety) and IEC 61347 (drive power safety).
7. Reference Standards for LED Strip Testing
IEC 62560: International safety standard for LED strip lights.
EN 62560: European standard of safety requirements for LED strip lights.
GB/T 36879: China’s national standard for LED strip lights.
UL 8750: American safety standard for LEDs and LED luminaires.
CE marking: Safety certification requirements for the European market.
Attention
●Target market priority: Select the corresponding certification according to the sales region (e.g., CE for EU, UL/FCC for US).
●Product segmentation: Different standards may apply to flexible LED strips, high-voltage/low-voltage LED strips, RGB LED strips, and so on.
●Certification organization: Choose an authoritative organization (e.g., SGS, TÜV, Intertek) for testing and certification.
LED strip testing ensures the safety, reliability, and performance of the product; helps consumers to choose the right LED strip; and provides a basis for LED strip manufacturers to control the quality of their products. With the continuous progress of LED technology and the diversification of market demands, the testing methods and standards for LED strip lights are constantly being updated and improved.