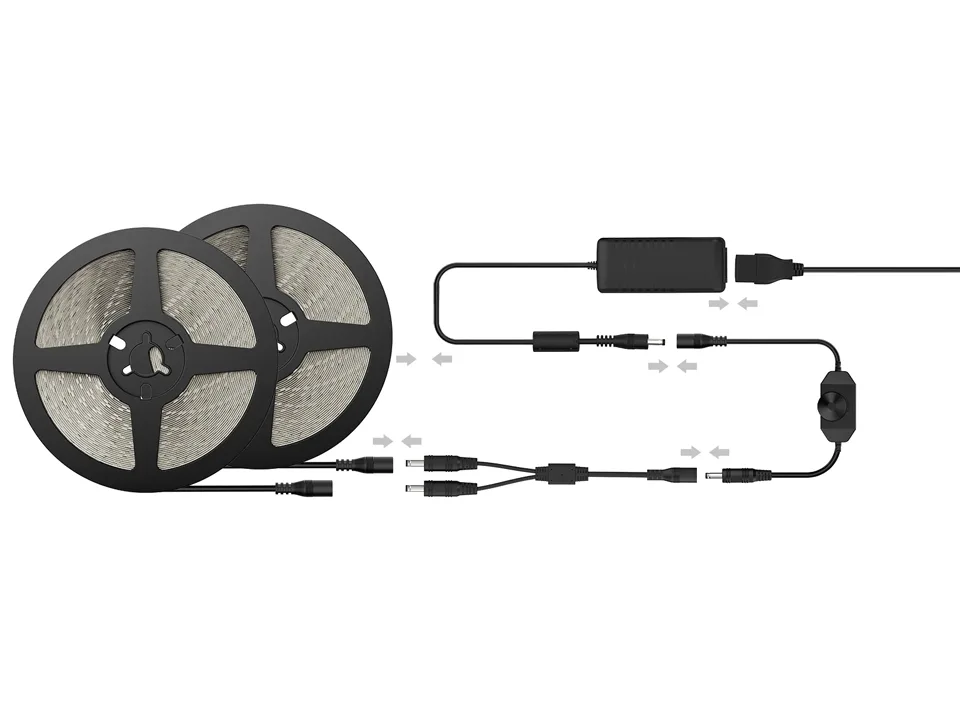
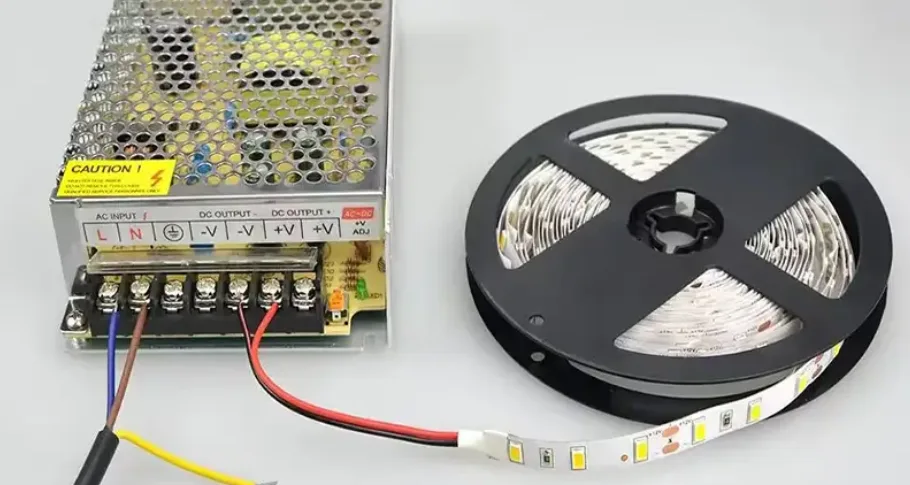
LED grow lights are an energy-efficient lighting solution designed to support plant growth by providing optimal light spectra. They offer benefits like low heat emission, long lifespan, and customizable wavelengths. This guide covers everything you need to know, including their principles, advantages, key parameters, and how to choose the right LED grow light.
What Is LED Grow Light
An LED grow light is an artificial light source designed to stimulate plant growth by emitting specific wavelengths of light optimal for photosynthesis. Utilizing light-emitting diodes (LEDs), these fixtures provide a targeted photosynthetically active radiation (PAR) spectrum, enhancing chlorophyll absorption and promoting photomorphogenesis. Compared to traditional grow lights, LEDs offer higher photon efficacy, lower heat output, and a customizable spectrum, improving plant yield and energy efficiency. Their ability to emit precise red (600–700nm) and blue (400–500nm) wavelengths makes them ideal for various growth stages, from vegetative development to flowering.
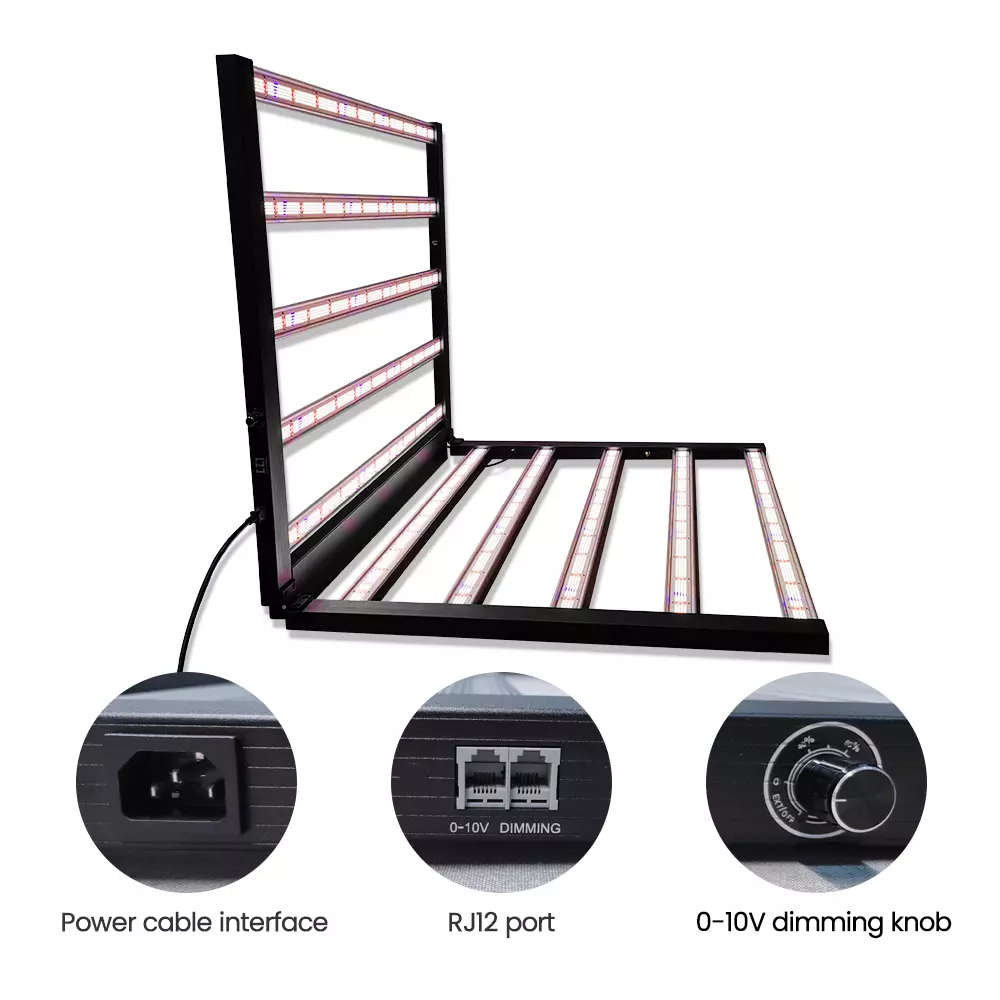

1000W Foldable LED Grow Light-G1000V1P06 Plus
Foldable fixture easy breeze to ship, store, and install, save costs
Full spectrum with 730nm IR and enhanced 460nm blue light
1000W high light intensity for higher yield
High efficacy to 2.8umol/J
Samsung LM281 diodes and SOSEN drivers
Compatible with UL1598/UL8800/DLC
Knob 0-10v dimming and RJ12 integrated control
5 years limited warranty
We are professional LED grow lights manufacturer from China, if you are looking for LED grow lights, please move to our web for me information www.kingrowlight.com
What’s The Technology Behind LED Grow Lights
LED grow lights use light-emitting diodes (LEDs) as their light source to promote plant growth. These LEDs emit specific wavelengths of light that plants need for photosynthesis. The technology behind LED grow lights involves selecting the optimal spectrum of light, often in the red, blue, and sometimes white ranges, to simulate natural sunlight for different plant growth stages.
LEDs are energy-efficient, producing more light with less heat compared to traditional grow lights like fluorescent or incandescent bulbs. This efficiency is achieved through semiconductor materials, which convert electrical energy into light. The diodes are also customizable, allowing growers to fine-tune the spectrum and intensity of light for various crops, making LED grow lights highly versatile.
Additionally, LED grow lights have a long lifespan and consume less electricity, making them cost-effective over time. They provide targeted light, reducing waste and ensuring that plants receive the right amount of energy for optimal growth.
What’s The Benifits of LED Grow Lights for Plant Growth
LED grow lights provide growers with the ability to fine-tune the light spectrum for optimal plant performance. By adjusting the balance of red, far-red, blue, and UV light, it’s possible to:
Enhance photosynthetic efficiency for better energy conversion.
Accelerate growth speed while maintaining plant structure.
Regulate flowering cycles to match desired production schedules.
Increase yield by promoting robust development and fruiting.
Improve quality through enhanced pigment production and nutrient profiles.

Red Light
Photosynthesis:
Red light (around 660 nm) is strongly absorbed by chlorophyll, making it a key driver in the photosynthetic process. This absorption boosts energy conversion, leading to improved carbohydrate production.
Growth Speed:
By optimizing energy production, red light encourages rapid cell division and leaf expansion. This helps plants achieve robust vegetative growth in a shorter time.
Flowering Cycle:
Red light plays an essential role in triggering flowering in many plant species. It helps regulate the photoperiodic responses that determine when a plant will begin flowering, ensuring a timely transition from vegetative to reproductive stages.
Yield:
With enhanced photosynthesis and optimal flowering, plants grown under red light can develop more fruiting sites and higher biomass, contributing to increased yield.
Quality:
Red light exposure can improve the overall quality of produce by promoting better pigment formation and more balanced nutrient allocation, resulting in plants with superior texture and flavor.
Far-Red Light
Photosynthesis:
Although far-red light (approximately 700–750 nm) is less efficiently absorbed by chlorophyll alone, it works synergistically with red light (the Emerson Enhancement Effect) to maximize photosynthetic efficiency.
Growth Speed:
Far-red light influences plant morphology by promoting elongation and expansion. When combined with red light, it can fine-tune growth speed, ensuring that plants develop with the right balance of height and sturdiness.
Flowering Cycle:
This wavelength plays a pivotal role in regulating the flowering cycle. Far-red light can trigger shade avoidance responses, which in turn affect the timing of flowering, helping to synchronize it with optimal environmental conditions.
Yield:
By optimizing the plant’s light environment, far-red light contributes to more efficient resource allocation. This can lead to an increase in overall biomass and, when managed correctly, a boost in yield.
Quality:
Proper management of far-red light can help produce more aesthetically pleasing and nutritionally robust plants. Its influence on plant structure and pigmentation can improve the visual appeal and internal quality of the produce.
Blue Light
Photosynthesis:
Blue light (in the 400–500 nm range) is critical for chlorophyll synthesis. It aids in the regulation of photosynthetic activity and supports overall plant energy production.
Growth Speed:
Blue light helps regulate plant architecture by controlling cell elongation. It often results in compact, sturdy plants with a balanced growth habit—ideal for reducing excessive stretching and promoting healthy development.
Flowering Cycle:
By influencing the plant’s internal clock, blue light can regulate the onset of flowering. It helps ensure that plants transition to the reproductive phase at the right time for maximum efficiency.
Yield:
A balanced blue light environment supports robust vegetative growth and, in turn, can lead to improved yields by ensuring that the plant’s foundation is strong before it enters the flowering and fruiting stages.
Quality:
Blue light enhances the development of pigments and secondary metabolites. This can translate into higher-quality produce with better color, flavor, and nutritional value.

Ultraviolet (UV) Light
Photosynthesis:
UV light (especially UV-B, 280–315 nm) is not a major contributor to photosynthesis. However, low levels of UV exposure can trigger protective responses that indirectly support the photosynthetic machinery by strengthening the plant’s overall health.
Growth Speed:
Exposure to controlled doses of UV light acts as a mild stressor, prompting plants to produce protective compounds. This “stress response” can sometimes lead to a more resilient growth pattern, though it needs to be carefully managed to avoid growth inhibition.
Flowering Cycle:
UV light can accelerate the development of certain flowering-related compounds, potentially shortening the time needed for a plant to reach its flowering stage. However, overexposure may disrupt normal developmental cycles.
Yield:
When applied in moderation, UV light can enhance the concentration of certain beneficial compounds that contribute to higher quality yields. This includes improved flavor and nutrient profiles. Excessive UV, however, might reduce overall yield due to cellular damage.
Quality:
One of the significant benefits of UV exposure is its ability to stimulate the production of secondary metabolites, such as flavonoids and antioxidants. These compounds enhance the color, taste, and nutritional profile of the produce, making it more appealing to consumers.
How to Choose The Right LED Grow Lights for Your Plants
Choosing the right LED grow lights involves a careful evaluation of several technical parameters—such as spectrum, efficacy, PPFD, and wattage—combined with an understanding of your specific plant types and their growth stages. Whether you are cultivating cannabis, vegetables, flowers, or succulents, tailoring your light selection to both the species and the phase of growth can dramatically enhance plant performance. By following these guidelines, you can create a lighting setup that maximizes photosynthetic efficiency, promotes healthy growth, and ultimately leads to better yields and higher quality plants
Key Parameters of LED Grow Lights
Spectrum
This refers to the range of wavelengths provided by the light. Plants require different light wavelengths—red for flowering, blue for vegetative growth, and sometimes UV or far-red to trigger specific responses. A balanced spectrum or adjustable spectrum options can be crucial depending on the plant’s needs.
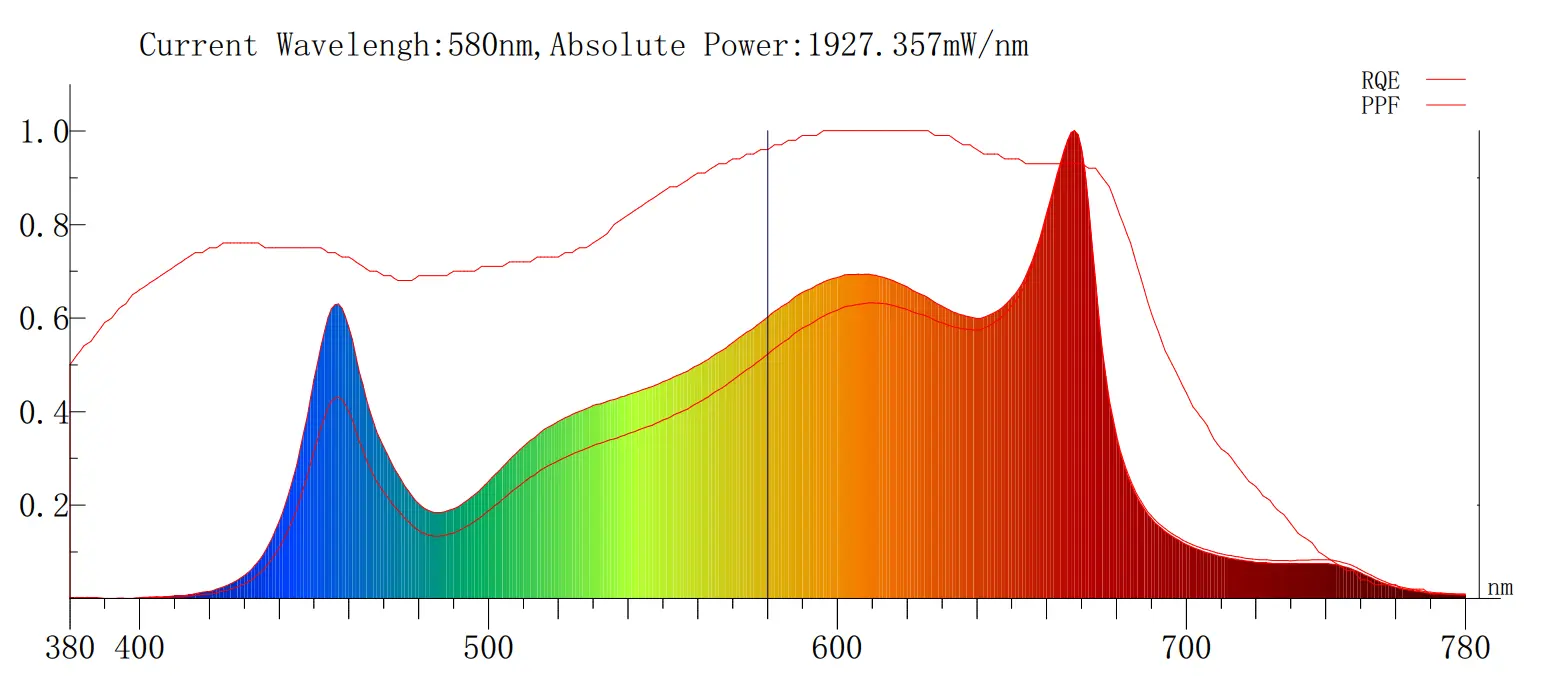
Efficacy
Measured in micromoles per joule (µmol/J), efficacy indicates how efficiently the light converts electrical energy into photosynthetically active radiation (PAR). Higher efficacy means more light is delivered to the plants per unit of energy, reducing electricity costs.
PPFD (Photosynthetic Photon Flux Density)
PPFD quantifies the amount of light (in µmol/m²/s) reaching the plant canopy. It is essential for determining if a plant is receiving enough light for optimal photosynthesis. Growers often look for lights that offer high PPFD values to ensure adequate energy delivery.
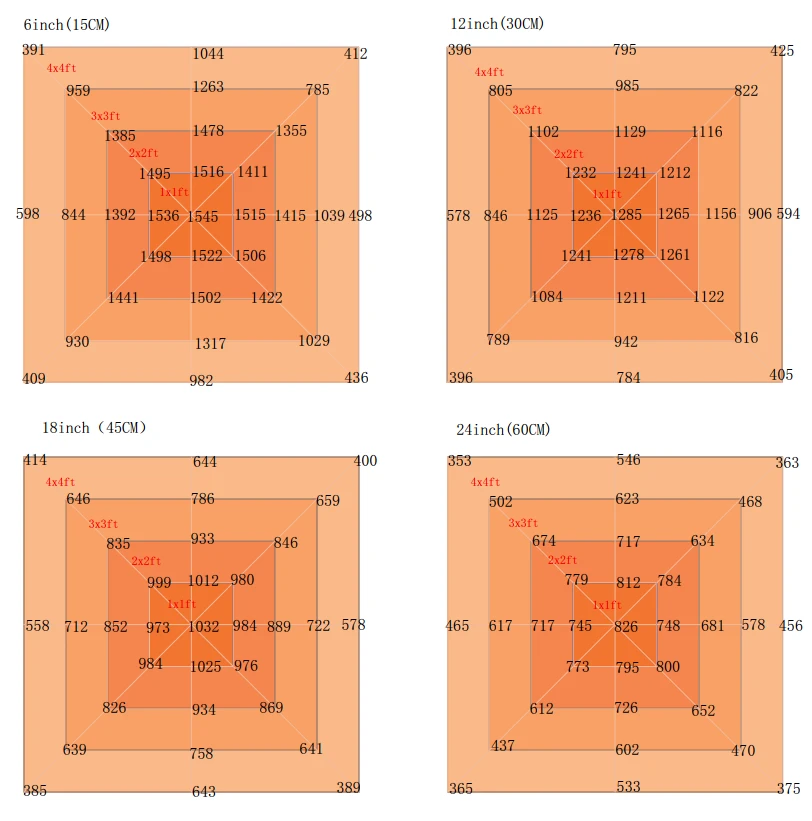
Wattage
This denotes the power consumption of the LED grow light. While higher wattage can be associated with stronger light output, it is also important to consider how it correlates with energy efficiency. Balancing wattage with efficacy and PPFD will help you choose a light that is both powerful and cost-effective.
Selecting LED Grow Lights Based on Plant Types
Different plants have unique light requirements, and selecting the right LED grow light can significantly enhance growth and yield. Here’s an analysis for a few common plant categories:
Cannabis
Cannabis plants benefit from full-spectrum lights that closely mimic natural sunlight. During the vegetative stage, a higher blue light component helps maintain compact growth, while red light becomes more important during the flowering stage to promote bud development. Adjustable spectrum LED lights that allow you to shift the balance between red and blue can be ideal for cannabis cultivation.
Vegetables
Vegetables generally thrive under lights that provide a balanced full spectrum. For leafy greens, an emphasis on blue light ensures strong, healthy leaves, while fruiting vegetables like tomatoes may require more red light during the fruiting phase. Look for lights with high PPFD and efficacy to support rapid growth and high yields.
Flowers
Flowering plants often require a spectrum that enhances both growth and blooming. A balanced mix that provides sufficient blue light for vegetative growth and red light for flowering can lead to more vibrant blooms and overall healthier plants. Some LED grow lights offer adjustable settings specifically tailored for different flowering needs.
Succulents
Succulents are typically more forgiving and require less intense light than other plants. However, they still benefit from a full spectrum that mimics natural sunlight. Lower wattage LED lights with an emphasis on balanced spectral output can help maintain the compact structure and vivid coloration of succulents without causing stress or overheating.
Tailoring LED Grow Lights to Growth Stages
The lighting requirements for plants change as they progress from one growth stage to another. Here’s how to adjust your LED grow light setup accordingly:
Seedling Stage
During this early stage, gentle light with a higher percentage of blue wavelengths is crucial. Blue light supports strong, healthy root and shoot development without causing damage to delicate seedlings. Look for LED lights with lower PPFD values and reduced wattage to provide a soft start for young plants.
Vegetative Stage
As plants enter the vegetative stage, they require a higher intensity of light to support rapid growth and foliage expansion. A balanced spectrum that still maintains a healthy dose of blue light is key, but an increase in overall light intensity and PPFD will boost photosynthesis and energy production. Adjustable lights or systems with modular options are ideal during this phase.
Flowering Stage
For the flowering or fruiting stage, the balance shifts towards red wavelengths, which are essential for bud formation and fruit development. Increasing the red light component helps trigger the photoperiodic responses that lead to flowering. Many LED grow lights offer a “flowering mode” that optimizes the spectrum for this stage. High PPFD remains critical to ensure that the plants receive enough energy to maximize yield and improve the quality of the produce.