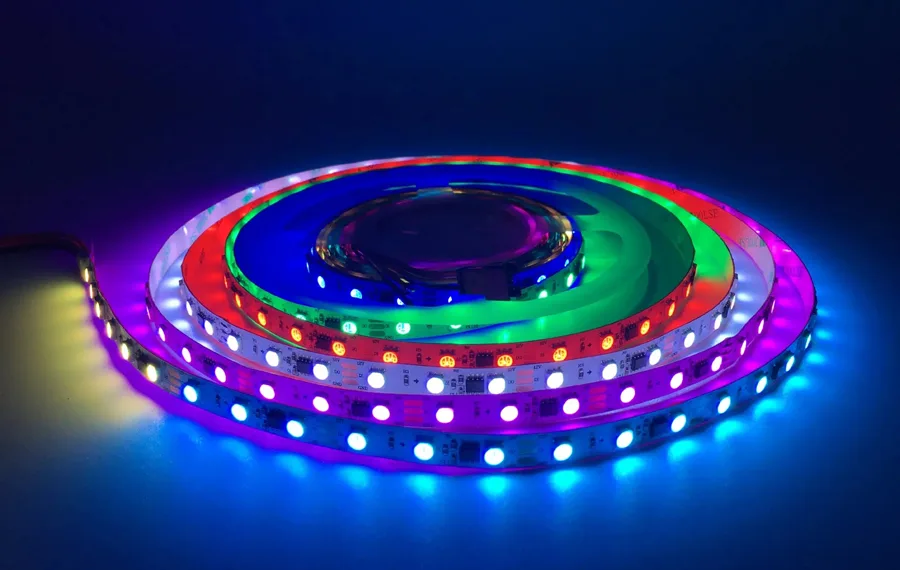
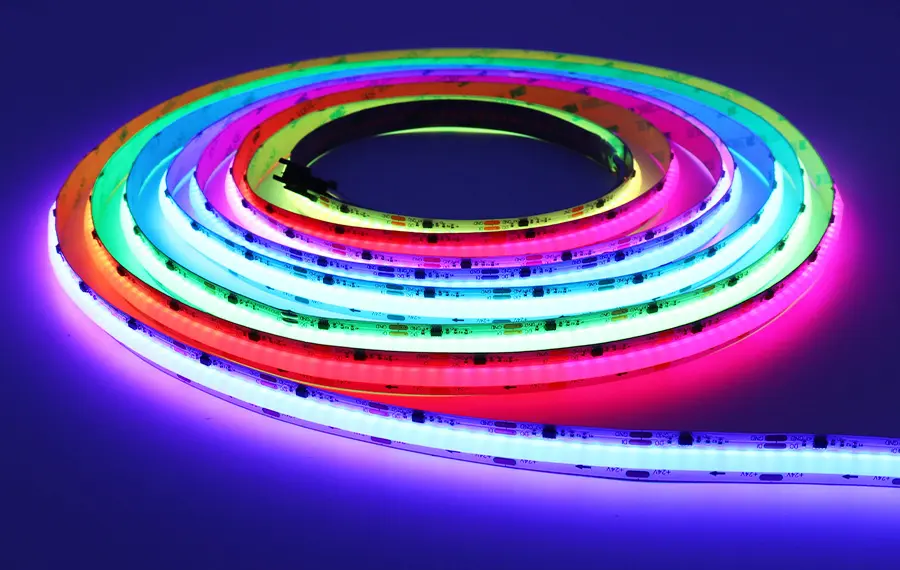
In today’s lighting technology landscape, LED strips have gradually become the mainstream choice due to their efficiency, energy-saving features, and long lifespan. Among these, addressable LED strips stand out for their unique personalization and programmability, offering unprecedented flexibility and creative potential in lighting design. Each LED or group of LEDs in these strips can be individually controlled by either built-in or external IC, allowing for complex and varied lighting effects.
But how do these magical IC work? How do they play a central role in addressable LED strips? This article will introduce you to the different types of addressable LED strips and IC available on the market, giving you an in-depth understanding of their types, features, working principles, and how to select and configure them.
What is an Addressable LED Strip?
An addressable LED strip is a type of digital strip that includes a flexible circuit board, LEDs, and driver chips. The term “addressable” refers to the ability to control the color and brightness of each LED or group of LEDs individually, thanks to the integrated circuit (IC) embedded in or connected to each LED.
Addressable LED strips come in various forms, including different lengths, LED densities (the number of LEDs per meter), and color functionalities, ranging from RGB (Red, Green, Blue) to RGBW (Red, Green, Blue, White) for enhanced color mixing and white light options.
The placement of the addressable LED IC is mainly divided into two types: one is a miniature IC built into the LED structure, and the other is an IC placed externally to the LED. Below is an image of an addressable LED strip:
What are Built-in IC and External IC?
A built-in IC refers to an integrated circuit within the LED’s internal circuitry, reducing the need for external circuit design, components, and production costs. A single IC can control a single LED, achieving multiple color changes.
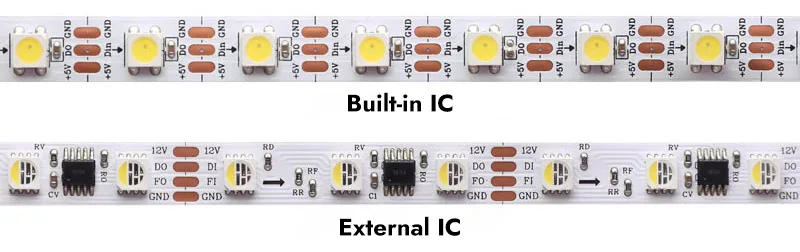
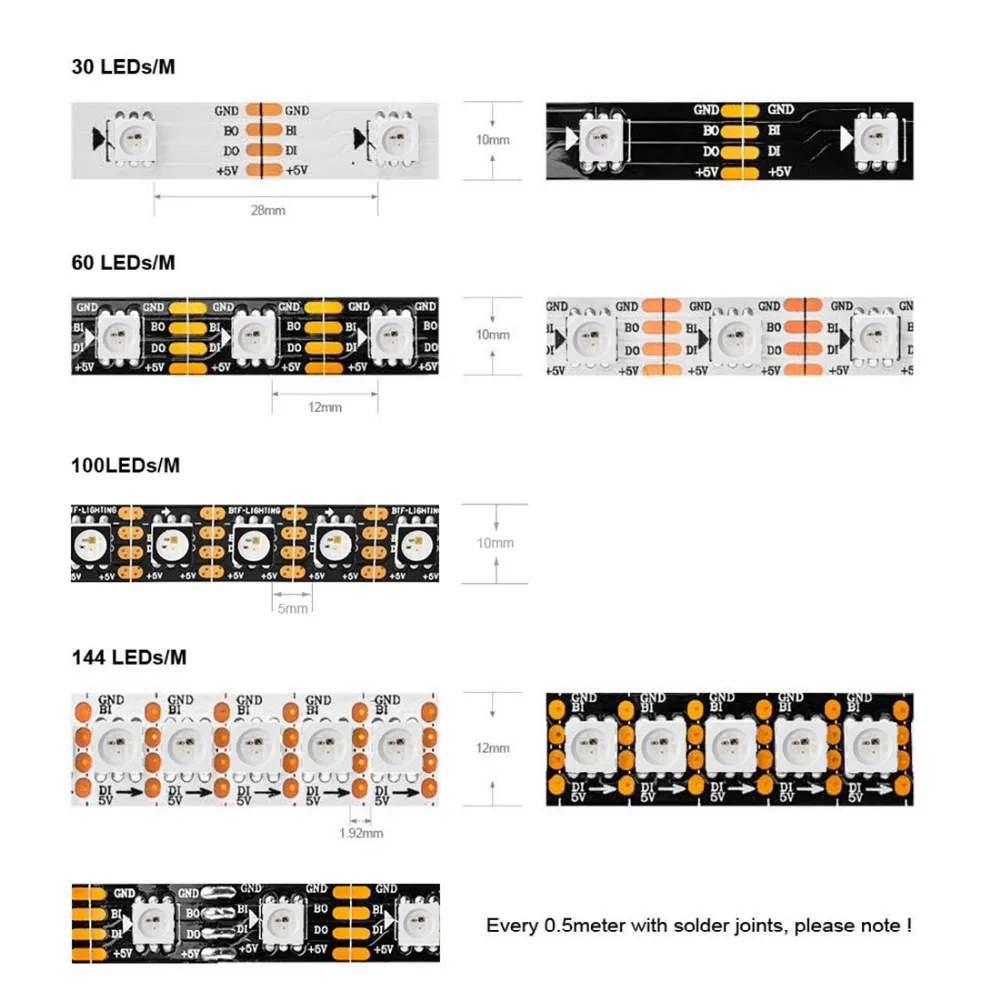
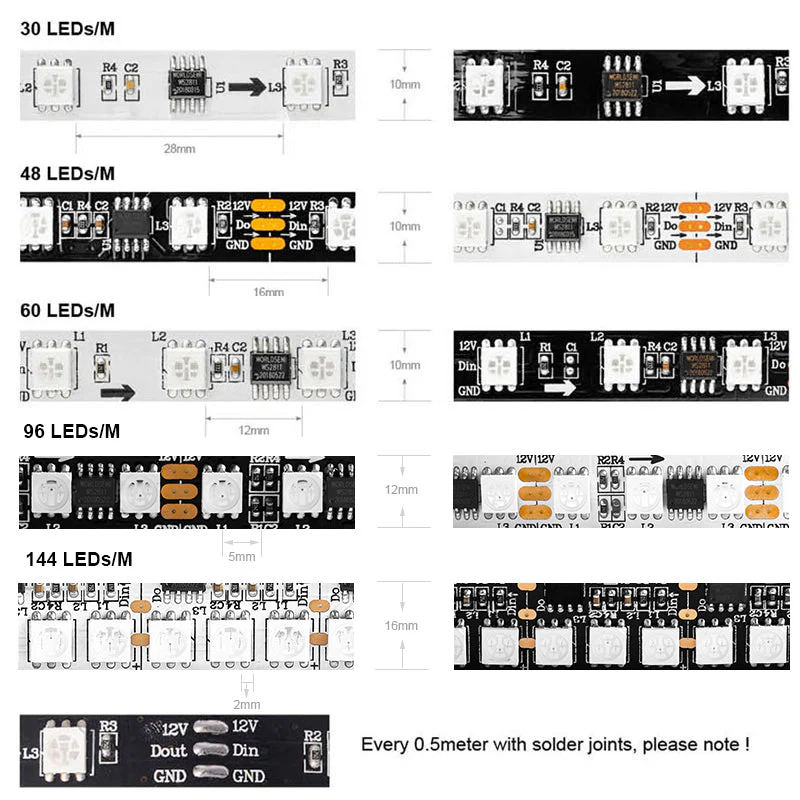
An external IC, on the other hand, is the more commonly seen standalone integrated circuit. This external design offers greater flexibility in terms of maintenance and customization, as individual components can be more easily replaced or modified. One external IC typically controls one or more LEDs, usually three or six.
Types of Addressable IC
Addressable IC can be classified based on their control protocols into DMX512 IC and SPI IC. DMX512 is an international standard protocol, meaning different models of DMX512 IC might have varying performance, but they support the same protocol. This means that a single DMX512 controller can control different types of DMX512 IC. However, SPI is not an international standard protocol, and different manufacturers’ SPI IC support different protocols, meaning different SPI IC may require different SPI controllers.
Common SPI built-in IC models: WS2812B, WS2813, WS2815, SK6812, SK9822, APA102, APA107, etc.
Common SPI external IC models: WS2801, WS2811, WS2814, WS2818, UCS1903, TM1812, TM1814, TM1914, TM1934, LPD6803, LPD8806, etc.
Common DMX512 external IC models: TM512, UCS512, etc.
Related IC datasheet download:
IC Feature Comparison
| IC Type | Voltage | Control Unit | Picture | Feature |
| WS2811 (External IC) | DC12V | 1 IC driver 3 LEDs |  | 12V working voltage convenient wiring |
| WS2812B (Built-in IC) | DC5V | 1 IC driver 1 LEDs |  | Best sale individually addressable pixel led strip |
| WS2813B (Built-in IC) | DC5V | 1 IC driver 1 LEDs |  | WS2812B updated, dual signal wires breapoint resume function |
| WS2815 (Built-in IC) | DC12V | 1 IC driver 1 LEDs |  | Dual signal wires breapoint resume function |
| SK6812 (Built-in IC) | DC5V | 1 IC driver 1 LEDs |  | RGB+White, RGB+Warm White, RGB+Natural White |
| TM512AC (External IC) | DC12V | 1 IC driver 3 LEDs |  | Direct connection to the DMX console, online address writing, breapoint resume |
| UCS512C (External IC) | DC24V | 1 IC driver 6 LEDs |  | Direct connection to the DMX console, online address writing, breapoint resume |
Types of Addressable LED Strips
Addressable LED strips can be divided into four types based on the signal type of the built-in or external IC: single-signal strips, dual-signal strips, breakpoint continuation series, and DMX512 strips, each with distinct characteristics.
Single-Signal Addressable LED Strips
Single-signal addressable strips can only operate through one signal, where one IC controls a region called a pixel. If one pixel fails, other pixels stop working, as the connection includes only one positive wire, one negative wire, and one signal wire.
1. 12V: positive wire.
2. Din/Do: data signal wire.
3. GND: negative wire.
| 3pin Single Signal | Color Support | IC Type | LED Type | Voltage Support | IC Control Unit |
| WS2812B | RGB | Built-in IC | 5050 | 5V | 1 LEDs |
| SK6812 | White /RGB / RGBW | Built-in IC | 5050 | 5V/12V/24V | 1/3/6 LEDs |
| WS2811 | White/RGB/RGB+W/RGB+CCT | External IC | 5050 | 5V/12V/24V | 1/3/6 LEDs |
| UCS1903 | RGB | External IC | 5050 | 5V/12V/24V | 1/3/6 LEDs |
| TM1812 | White /RGB / RGBCCT | External IC | 5050 | 12V/24V | 3/6 LEDs |
| TM1814 | RGBW | External IC | 5050 | 12V/24V | 3/6 LEDs |
| TM1936 | RGBCCT | External IC | 5050 | 24V | 6 LEDs |
| WS2814 | RGBW | External IC | 5050 | 24V | 6 LEDs |
Dual-Signal Addressable LED Strips
Dual-signal addressable LED strips include a clock function in addition to the data signal, allowing the LEDs’ lighting time to be set.

1. GND: negative wire
2. CI/CO: clock wire
3. DI/DO: digital signal wire
4. 5V: positive wire
| 4pin Dual Signal | Color Support | IC Type | LED Type | Voltage Support | IC Control Unit |
| SK9822 | RGB | Built-in IC | 5050 | 5V/12V/24V | 1/3/6 LEDs |
| APA102 | White/RGB | Built-in IC | 5050 | 5V/12V/24V | 1/3/6 LEDs |
| WS2801 | RGB | External IC | 5050 | 5V/12V/24V | 1/3/6 LEDs |
| LPD8806 | RGB | External IC | 5050 | 12V/24V | 3/6 LEDs |
| LPD6803 | RGB | External IC | 5050 | 12V/24V | 3/6 LEDs |
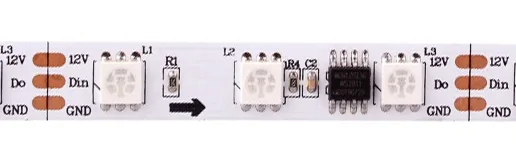
Breakpoint Continuation Addressable LED Strips
Breakpoint continuation is an upgraded version of single-signal addressable LED strips. It features a 4-channel dual data line control circuit with a data line and a backup data line. If the single data line fails, the backup data line automatically activates, ensuring uninterrupted signal transmission.
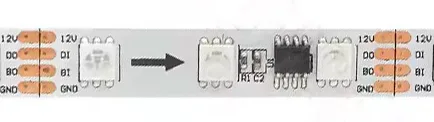
1. 12V: positive wire
2. DI/DO: digital signal wire
3. BI/BO: backup line
4. GND: negative wire
| 4pin Breakpoint Resume | Color Support | IC Type | LED Type | Voltage Support | IC Control Unit |
| WS2813 | RGB/RGBW | Built-in IC | 5050 | 5V | 1 LEDs |
| WS2815 | RGB | Built-in IC | 5050 | 12V | 1 LEDs |
| WS2818 | RGB/RGBW | External IC | 5050 | 12V/24V | 3/6 LEDs |
| TM1914 | White/RGB | External IC | 5050 | 12V/24V | 3/6 LEDs |
| WS2814 | RGBW | External IC | 5050 | 12V/24V | 3/6 LEDs |
DMX512 LED Strips
DMX512 LED strips differ from other addressable LED strips in that they are more intelligent and can connect to DMX systems, controlling various effects like chasing, running, animation, and more, with customizable patterns and colors.
If a pixel fails, the signal transmission is not affected, and other pixels can function normally.

1. 24V: positive wire
2. PI/PO: address programming
3. A: digital line
4. B: digital line
5. GND: negative wire
| 5pin DMX512 | Color Support | IC Type | LED Type | Voltage Support | IC Control Unit |
| TM512AC | RGB/RGBW | External IC | 5050 | 5V/12V/24V | 1/3/6 LEDs |
| UCS512C | RGB/RGBW | External IC | 5050 | 5V/12V/24V | 1/3/6 LEDs |
If you find the above markings on your LED strip, it means your strip is addressable, and you can control it in different modes.
If you would like to know about specific products, please click here.
How Do Addressable LED Strips Work?
To run an addressable LED strip, you’ll need several key components:
1. Addressable LED strip (SPI/DMX)
2. Controller (SPI/DMX)
3. Power supply (DC5V/12V/24V)
The IC chip on the addressable strip receives digital signal data from the LED controller and then transmits the control instructions to each LED.
An IC can control one or multiple LEDs, and different control commands can be sent to each IC, allowing adjacent IC-controlled regions of LEDs to have different colors and brightness levels, enabling complex lighting effects.
How to Choose the Right Addressable LED Strip?
Selecting the right addressable LED strip depends on your specific needs and application. Here are some factors to consider when choosing an addressable LED strip:
Voltage: Addressable LED strips are available in 5V, 12V, and 24V options. Lower voltages (5V) are typically used for shorter strips or single LED projects, while higher voltages (12V, 24V) are better suited for longer runs as they help reduce voltage drop.
LED Density: LED density refers to the number of LEDs per meter on the strip, ranging from 30 LEDs/m to over 144 LEDs/m. When selecting LED density, you should consider the application and environment of the LED strip. For example, if you’re using the strip for accent lighting in a small space, lower LED density may be sufficient. For primary lighting or larger spaces, higher LED density may be more appropriate.
Color Type: When choosing the color of an addressable LED strip, it’s important to consider the atmosphere you want to create and the intended use of the lighting. Depending on the color, addressable LED strips come in several types. The most common types include:
o Monochrome: Produces only one color, such as white, red, green, blue, etc.
o RGB: Can emit red, green, and blue colors, which can be combined to produce various colors.
o RGBW: Can produce pure white in addition to RGB colors.
o RGBWW: Equipped with both warm white and cool white LEDs in addition to RGB colors.
Can Addressable LED Strips Be Cut?
Yes, you can cut addressable LED strips, but it’s essential to keep a few critical points in mind to ensure the strip’s functionality is maintained after cutting.
Addressable LED strips typically have designated cutting points marked by a line or sometimes with a scissor icon on the strip. The cutting unit is closely related to the number of LEDs controlled by one IC, typically 1, 3, or 6 LEDs per IC. Thus, you can cut one LED, three LEDs, or six LEDs. Addressable strips with a cutting unit of one LED are often referred to as individually addressable LED strips.
In summary, addressable LED strips are becoming increasingly popular due to their versatility, ease of use, and wide range of applications. When choosing the right addressable LED strip for your project, it’s important to consider factors such as IC type, LED color, strip connection length, and the LED controller and driver. Taking the time to understand your project’s needs and selecting high-quality components can ensure that your expectations are met and provide beautiful, customizable lighting effects. If you have any questions, please consult our sales engineers!
Related Posts
Pixel Addressable LED Strip Comparison: DMX512 vs. SPI
Ultimate Guide to Programmable LED Strips
WS2812B LED Strip VS SK6812 LED Strip: Which is Better?
WS2812 VS WS2813 LED Strip Light
How does DMX control the LED strip light? and how to connect them?






