With the popularization of smart buildings and smart homes, lighting control has become an indispensable part of them. KNX and DMX512 are two commonly used lighting control protocols, which are widely used in smart homes and stage lighting, respectively. So, is it possible to use DMX512 in the KNX control system? The answer is yes. Thanks to advances in the microprocessor industry, it is possible for these two different protocols to establish a link between them via KNX-DMX gateway devices. This article will examine the characteristics of both protocols, their comparative analysis, and their integration via a gateway.
What is KNX?
KNX is the world’s standard communication protocol for intelligent home and building control. The system has been in use for 25 years and is a proven performer in the field of KNX building automation. Systems equipped with the KNX protocol technology can easily help you to control household appliances remotely from a single touch panel. As a result, it is nowadays used in a wide range of buildings: private homes, commercial complexes, industrial buildings, universities, hospitals, and many others.
The KNX protocol was developed by the KNX Association to integrate and control several systems in a building, such as heating, lighting, and access control, from a central computer. More than 500 manufacturers worldwide have developed KNX-based equipment for the HVAC, lighting, and security industries. Because KNX-based systems guarantee forward and backward compatibility of products on existing bus networks, system designers can easily select quality-based devices or replace them with devices from other manufacturers if they have design flaws or are out of stock.

KNX Lighting Control Devices
KNX offers a variety of devices designed for lighting control in intelligent building automation. These devices are designed to work seamlessly with the KNX protocol to provide advanced control and management of the lighting system.
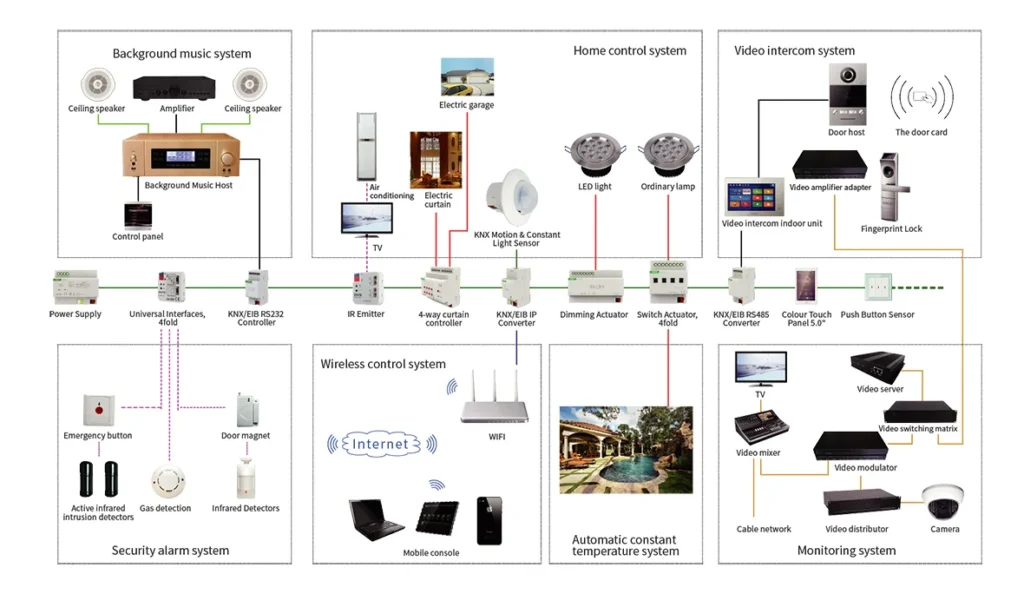
KNX is a decentralized system, which means that if one device stops working, the rest of the devices will continue to operate unimpeded. KNX is a wired system, where all KNX devices are connected to the KNX bus.The KNX system consists of 5 components, namely the KNX power supply, the KNX bus, the KNX actuators, the KNX sensors, and the IP interface.
1. KNX Power Supply: The KNX power supply is a key component in the KNX lighting control system, providing power to the KNX bus and enabling communication between the different KNX devices. It ensures a stable and reliable distribution of power to all KNX devices for proper operation.
2. KNX Bus: In its simplest form, this is a twisted pair (TP) or a 2-core cable. In KNX TP, the bus cable provides data and power to all bus devices.
3. KNX Sensors: KNX sensors are used to detect various environmental parameters such as motion, light levels, temperature, and humidity and provide feedback to the KNX system. This information can be used to trigger lighting scenes, adjust dimming levels, or activate other automation functions, making the lighting system more energy-efficient and user-friendly.
4. KNX Switching Actuators: KNX switching actuators are used to control lighting circuits, enabling on/off switching, dimming, and scene control. They can be mounted on distribution boards or directly behind light switches for local and remote control of lighting circuits.
5. IP Interface: It is a KNX device that connects to a WiFi router and the KNX bus. It is a KNX device that connects to a WiFi router and the KNX bus. With this device, the KNX system integrator can program all sensors and actuators via the ETS software.
Disadvantages of KNX
1. System integrators who require a special KNX license install and program the system via the ETS KNX proprietary software. Therefore, any time you need to change the configuration or replace any device, you must call the KNX system integrator.
2. KNX does not offer integration with home automation standards such as Apple HomeKit, Google Home, or Amazon Alexa. A third-party service is required.
What is DMX512?
DMX512 is a digital signaling protocol that allows the control of lighting equipment, including LED strips, via digital signals. The DMX512 protocol was developed by the United States Institute of Theatrical Lighting (USITT) to provide a standard communication protocol between lighting controllers and lighting equipment. The protocol allows the user to send signals through the console to precisely control various parameters of the lighting equipment, such as brightness, color, and motion patterns.
DMX lighting control stands for Digital Multiplexing and is a digital control protocol used primarily in theatrical spaces. Over the past few years, DMX lighting fixtures have made their way into the architectural realm to perform a variety of functions, from illuminating the exteriors of buildings, bridges, and works of art to easily changing the ambiance of an interior space by altering the color temperature of the white light.
This type of application typically involves a more powerful DMX lighting control system and often requires integration with other systems within the building for global control. However, once programmed, these shows can be recalled, like lighting scenes, or overridden by static color selection from a keypad or touchscreen.

DMX Lighting Control Devices
The DMX512 is a centralized system, i.e., the system is controlled by a master controller. In this system, all lighting devices or their decoders are daisy-chained and serially addressed, with only the first lighting device connected to the DMX Master Controller.The DMX system consists of 4 components: the DMX Master Controller, the DMX Universe, the DMX Decoder, and the Lighting Devices.
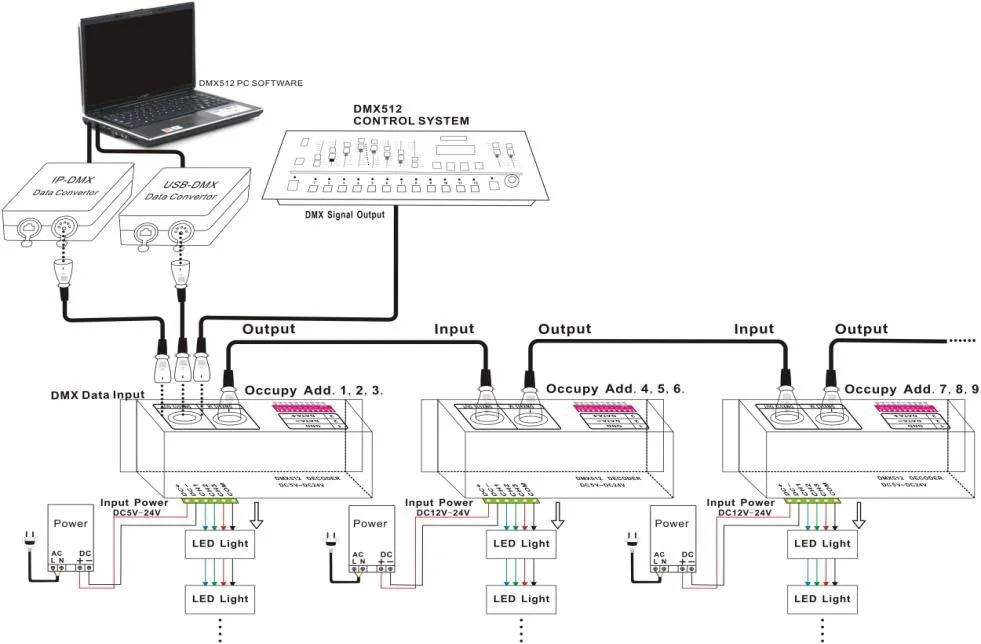
1. DMX Master Controller: This is also known as the DMX console and is the heart of the DMX system. This is where one can control the lights by interacting with the system via a computer or touch screen.
2. DMX Universe: All DMX decoders are connected to a single DMX master using a daisy-chain connection method using three wires (Data +, Data -, and Common) as shown in the diagram above, which is referred to as a single DMX domain. There are 512 control points available in a single domain, i.e., 512 lighting fixtures can be turned on or off.
3. DMX Decoder: The type of DMX decoder depends on the lighting fixture it controls. They process the DMX master signal and control the connected lighting fixtures.
4. Lighting fixtures: LED spotlights, RGB/RGBW strips, addressable LED strips, 2-axis 360-degree rotating laser lights, and more.
Disadvantages of DMX
1. Centralized systems have a single point of failure, the DMX Master.
2. Daisy chain points of failure: if a single decoder fails or is removed from the chain, subsequent decoders will stop working.
3. Sensor integration cannot be used directly.
KNX vs. DMX, which is better?
KNX and DMX each have their own strengths and are suitable for different scenarios; KNX is better suited for overall control of smart homes and building automation, while DMX is better suited for lighting control that requires real-time, frequent changes.
Although both protocols were originally designed to suit different applications, due to advances in the microprocessor industry, these protocols have invaded each other’s space, so they can be compared on certain common parameters in the chart below.
| PARAMETER | KNX | DMX |
| System architecture type | De-centralised | Centralised since depends on Master Controller |
| Communication | Bi-directional. Hence health of devices could be known | DMX is unidirectional. DMX RDM is bidirectional |
| Fault finding of devices possibility | Yes | No |
| Manufacturer device certification required | Yes, devices need to be certified by KNX labs/association | Not required |
| Compatibility of devices between different manufacturers | Yes. Ensured by certification. | No |
| System Integrator requirements | Should be certified by KNX | No such requirement |
| Programming or changing configuration | Requires ETS software and System Integrator | Can be changed via controller, no expertise required |
| Number of devices on single bus line | 256 | 512 |
| Communication rate | 9600 bps | 250,000 bps |
| Other system integration | Yes. Such as HVAC, Security, Energy Management | No. Limited to lighting only. |
| Extreme lighting effects | No | Yes |
| Security | KNX Secure | No |
| Cost | KNX Direct less cost | Low system cost compared to both |
| Application | Building automation, Lighting automation, Commercial automation, Energy management | Stage lighting, theatre lighting billboards, signages, building facade lighting. Multi coloured effect lighting. |
The Bridge Between KNX and DMX: KNX-DMX Gateway
Although KNX and DMX have their own areas of application, sometimes it is necessary to use them together for integrated control of home and stage lighting. In this case, the two can be interconnected by means of the KNX-DMX Gateway, a device that connects the KNX and DMX protocols and allows the devices in the KNX system to control the DMX devices, thus enabling fine control of stage lighting and ambient lighting.
The KNX-DMX Gateway is a gateway between KNX and DMX512 and can be configured with up to 64 channels (some brands offer 48 channels). DMX is a protocol used for lighting control and is particularly suitable for stage technology.
The device allows easy control of DMX lights, e.g., using KNX buttons. Up to 64 dimmer channels or 8 RGB/RGBW channels are available. Each channel can be assigned several subsets of DMX512 addresses. The dimmer channels can be switched. One or more DMX devices can be dimmed via KNX. The RGB/RGBW channels can control RGB/RGBW-capable DMX devices. Each RGB color and each HSV attribute can be controlled individually via KNX. Each channel can be linked to up to 8 scenes with any brand of KNX device. In addition, few brands have 4 sequencers in the gateway to perform more complex tasks.
In some manufacturers, KNX actuators can be controlled via DMX. For example, room lighting as part of a KNX installation can be controlled via the DMX Lighting Control Panel. Up to 64 DMX512 addresses can be evaluated individually and sent to KNX. dimming values, switches with switching thresholds, and RGB values can be interpreted.
Example of a KNX-DMX gateway application:
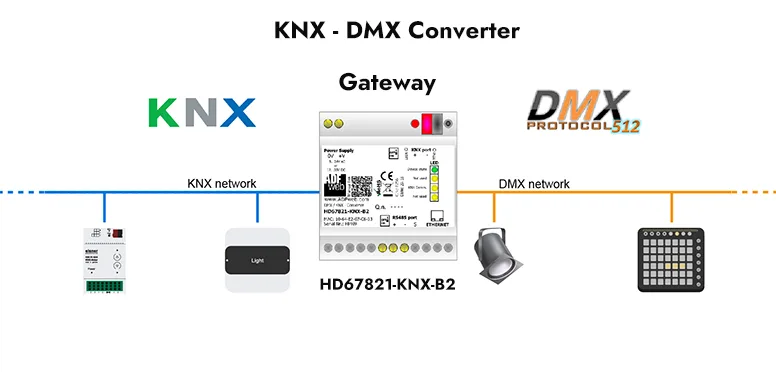
KNX-DMX gateway wiring example:
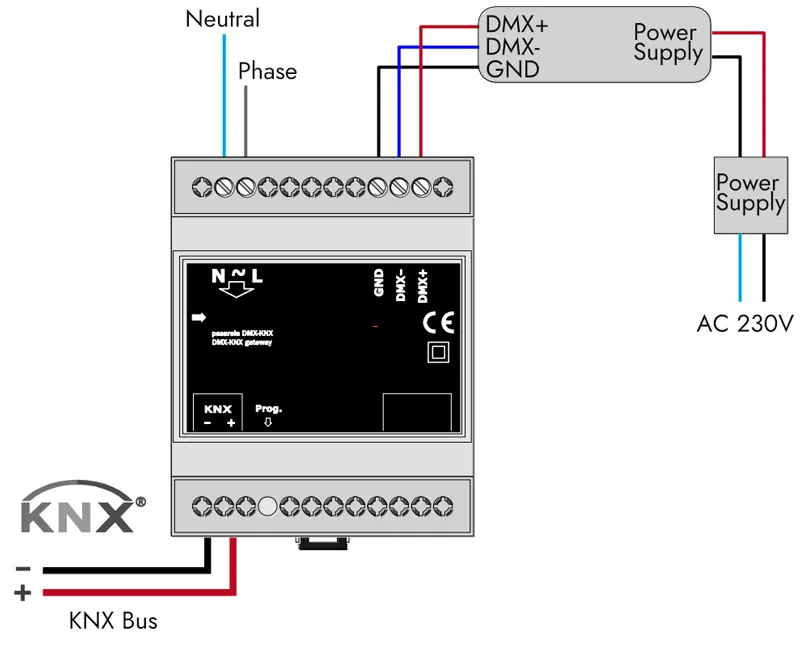
The transmission line must be terminated with a 120 Ohm/0.25 W resistor at the last receiver of the DMX512 transmission path. This resistor must be inserted directly between the two signal lines before the input of the last receiver circuit. Only twisted-pair shielded cable should be used for DMX.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the KNX lighting control system offers a powerful and versatile solution for intelligent building automation. From different types of lighting control options, including power dimming, 1-10V dimming, DALI, KNX LED drivers, and DMX, to a wide range of KNX lighting control devices, such as power supplies, switching actuators, sensors, and LED drivers, KNX technology offers a comprehensive range of features for efficient and effective lighting control.
Related Articles:
Guide to KNX Smart Control Systems
How does DMX control the LED strip light? and how to connect them?




